How Is Agentic AI Different From Traditional Automation? A Complete Guide
The Revolution You Need to Understand
The world of automation is changing rapidly, and if you've been paying attention to the latest developments in artificial intelligence, you've probably heard the term "agentic AI" popping up everywhere. But here's the real question: what exactly is agentic AI, and more importantly, how is agentic AI different from traditional automation?
This distinction matters more than you might think. While traditional automation has been the backbone of business efficiency for decades, agentic AI represents a fundamental shift in how machines work, learn, and solve problems. Understanding this difference could be the key to staying competitive in your industry, whether you're in customer service, data management, testing, or any other field that relies on automated processes. https://yourblog.com/hugging-face-democratizing-ai
Let's explore what makes agentic AI truly revolutionary and why businesses around the world are starting to take notice.
The Core Difference: More Than Just Robots Following Orders
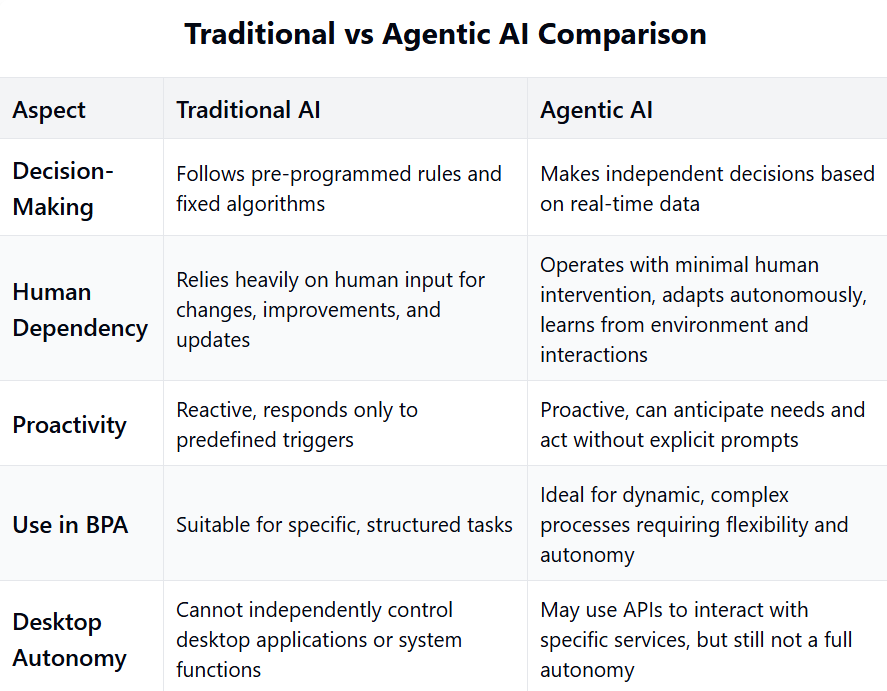
At its heart, the answer to "how is agentic AI different from traditional automation" comes down to one powerful concept: intelligence.
Traditional automation is like having a very obedient robot that follows a precise recipe. You tell it exactly what to do, step by step, and it does it perfectly—every single time. But the moment something unexpected happens, or the recipe changes even slightly, the robot gets confused and stops working.
Agentic AI, by contrast, is more like having an intelligent assistant who understands your goals and can figure out the best way to achieve them, even when circumstances change. Instead of just following fixed rules or scripts, it can reason about goals, plan multi-step actions, adapt to changing conditions, and improve over time with less human reprogramming. Source This is the fundamental transformation happening in the automation space right now.
Understanding Decision-Making: The Brain of the Operation
How Traditional Automation Makes Decisions
Traditional automation follows predefined rules, scripts, and workflows. It does exactly what it was programmed to do and fails or stops when conditions change or exceptions occur. Source Source Source
Think about a typical example: an RPA (Robotic Process Automation) bot that clicks through the same user interface steps every time, or a rules-based email auto-responder that sends the same response to every inquiry. These systems are brilliant at repetitive tasks, but they're essentially mindless. They can't think. They can't adjust. They can't problem-solve.
If the user interface changes even slightly, that RPA bot becomes useless. If an email requires a slightly different response, the auto-responder sends the wrong answer. It's like asking someone to follow directions to a restaurant, and they get completely lost if one road is closed.
How Agentic AI Makes Decisions
Agentic AI uses context-aware, goal-driven decision-making. It can choose among options, set sub-goals, and adjust its strategy in real time to achieve an outcome. Source Source Source
More importantly, agentic AI combines reasoning, planning, and execution instead of just executing a static script. Source Source https://yourblog.com/oracle-fusion-ai-agent-studio-1z0-1145-1
This is a game-changer. An agentic AI system can look at a complex customer service situation, understand what the customer actually needs, access multiple systems to find the right solution, and then take action—all without asking a human for help. It doesn't just follow a script; it reasons through the problem.
Autonomy and Goal Orientation: The Freedom Factor
Traditional Automation: Task-Focused and Dependent
Traditional automation is typically task-oriented, which means it automates discrete, repeatable steps. Source For example, it might copy data from one system to another, or process a standard form. The work is broken down into specific tasks, and each task is automated individually.
The critical limitation? Traditional automation requires humans to define every workflow, handle exceptions, and adjust logic whenever something changes. If something goes wrong—an exception occurs—the system stops and waits for a human to intervene. There's no independent problem-solving happening.
Agentic AI: Goal-Focused and Independent
Agentic AI is goal-oriented. You give it an objective like "resolve this support ticket" or "optimize inventory," and it breaks that goal down into steps, chooses which tools and systems to use, and executes actions from start to finish. Source Source Source
Even more impressive, agentic AI can operate with minimal or no human oversight in many scenarios, including handling exceptions. Source It doesn't need constant supervision. It can make decisions, adapt its approach, and solve problems on its own.
This is the kind of autonomy that could completely transform how businesses operate. Instead of having processes constantly monitored by humans, intelligent agents could handle the work independently.
Learning and Adaptability: The Evolutionary Advantage
Traditional Automation: Frozen in Time
Traditional automation is static—it doesn't learn. Any change in process, user interface, data format, or business rules usually requires manual reprogramming or script updates. Source Source Source
This creates a significant problem: traditional automation is brittle in dynamic environments. Downtime and maintenance rise as processes evolve. Source Source
Imagine running a business where every time something changes—a supplier updates their system, a customer's needs shift, a new product is introduced—your automation breaks down and requires IT specialists to fix it. The maintenance costs pile up, and the system becomes increasingly expensive to operate.
Agentic AI: Always Learning and Improving
Agentic AI learns from feedback and experience to refine its behavior and improve performance over time. Source Source Source
Additionally, agentic AI adapts in real time to new data, changing conditions, or unexpected events without explicit reprogramming. Source Source Source
This is revolutionary. A system that learns and adapts means lower long-term maintenance costs and better performance over time. The more it operates, the smarter it becomes.
One particularly exciting development is in the testing and automation space, where "self-healing" behaviors are emerging. For example, instead of using brittle selectors that break when a user interface changes, agentic systems use computer vision to recognize UI elements. This keeps automation flows working despite UI changes. Source It's like the difference between someone reading an address off a piece of paper versus someone who can actually see where they need to go and can navigate even if the landmarks change.
Scope and Complexity: What Each System Can Handle
Traditional Automation: Best for Simple, Stable Work
Traditional automation excels at simple, stable, high-volume processes with clear rules and low variability. Source Source Examples include data entry, scheduled jobs, and basic ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) operations.
However, it struggles significantly with multi-step, cross-system, or ambiguous tasks. If a process is complex or requires decision-making based on context, traditional automation hits a wall.
Agentic AI: Built for Complex, Dynamic Workflows
Agentic AI is designed for complex, dynamic workflows where decisions depend on context, patterns, or shifting goals. Source Source Source
More than that, it can coordinate across multiple systems and tools, manage multi-turn interactions, and proactively resolve issues. Source Source Source
This means agentic AI can handle situations that would completely baffle traditional automation. It can work across your entire business ecosystem, connect different systems, and solve problems that require creative thinking.
Human Involvement: Who's Really in Control?
Traditional Automation: The Human Dependency
Traditional automation is often semi-automatic, meaning humans design the process, handle edge cases and escalations, and frequently maintain scripts. Source Exception handling is typically routed back to humans, making it labor-intensive despite being "automated."
Think about it: if a system is breaking down regularly and requiring human intervention to fix exceptions, how automated is it really?
Agentic AI: Autonomous Operation
Agentic AI targets end-to-end autonomy for many use cases: detecting anomalies, choosing responses, and resolving issues without escalation when possible. Source
Humans still play a crucial role—you set the goals, constraints, and governance—but day-to-day operation can be largely agent-driven. This frees humans up to focus on strategic work rather than firefighting and maintenance.
Maintenance and Lifecycle: The Long-Term Picture
Traditional Automation: The Maintenance Burden
Traditional automation comes with high maintenance overhead. Scripts and rules break when UIs, APIs, or business rules change, leading to constant updates and downtime. Source Source
When you're scaling across many processes, this maintenance burden multiplies, making the system increasingly expensive to operate.
Agentic AI: Self-Optimizing Systems
Agentic AI is self-optimizing. Its learning and adaptation reduce the need for constant updates, lowering long-term maintenance costs. Source Source Source
It's much better suited to environments where data schemas, processes, or conditions shift frequently. Source Over time, this translates to significant cost savings and more reliable operations.
Real-World Examples: How This Plays Out in Practice
Customer Service: From Scripts to Intelligence
Traditional approach: IVR menus and scripted chatbots that follow fixed flows and escalate complex cases to humans. You've experienced this—you call a customer service line, navigate through menu options, and if your issue doesn't fit neatly into one of the predefined categories, you're transferred to a person.
Agentic approach: AI agents that understand multi-turn context, access your company's CRM and knowledge bases, personalize answers, and complete actions (refunds, rescheduling) autonomously. Source Source IBM has reported that such systems deliver faster responses and higher customer satisfaction. Imagine calling customer service and immediately speaking with an intelligent agent that actually understands your specific situation and can fix it on the spot. https://yourblog.com/rise-of-voice-agents
Testing and RPA: From Brittle to Resilient
Traditional approach: Selenium and Cypress scripts that fail when locators or UI layouts change, requiring manual fixes. Source Every time your development team updates the interface even slightly, test automation breaks.
Agentic approach: Vision-based agents that recognize UI elements, adapt to UI changes, and "self-heal," dramatically cutting test maintenance. Source The system literally sees what's on the screen and can figure out how to interact with it, even if the layout changes.
Data Integration and Operations: From Scheduled to Proactive
Traditional approach: Fixed ETL pipelines and scheduled jobs. When issues occur, they require manual investigation. You wait until the next scheduled run to discover problems, or someone notices something went wrong and has to dig into logs manually.
Agentic approach: Agents that monitor data flows, detect anomalies, propose or implement fixes, and evolve pipelines as data and schemas change. Source Problems are detected and often resolved before they impact your business.
Go-To-Market and Forecasting: From Static to Dynamic
Traditional approach: Static rules or reports updated on a schedule. Your forecasts are outdated the moment they're created, and adjusting strategy requires manual effort.
Agentic approach: Systems that learn from real-time GTM data, adjust forecasting models, and proactively support customer engagement strategies. Source Your forecasts stay accurate because the system continuously learns from new information.
When Should You Use Each Approach?
Understanding how agentic AI differs from traditional automation is important, but knowing when to use each is equally crucial.
Use Traditional Automation When:
Processes are stable, predictable, and rule-based. If you've got a process that rarely changes and has clear, defined steps, traditional automation works great.
You need deterministic behavior and regulatory transparency for simple tasks. In regulated industries, you often need to prove exactly why something happened. Traditional automation's predictability is valuable here. Source
Cost and implementation simplicity matter more than adaptability. Traditional automation is usually cheaper and easier to implement initially. Source
Use Agentic AI When:
Tasks are complex, cross-system, and dynamic. If you're dealing with multi-step processes that require decision-making, agentic AI is your answer.
Conditions, data, or goals change frequently and you want systems that can adapt without constant reprogramming. Source Source Source
You want proactive, goal-driven behavior rather than just scripted responses. Source
The Hybrid Approach: The Best of Both Worlds
Here's the exciting part: you don't have to choose just one. The best approach is often a hybrid strategy, where traditional automation handles simple, stable steps and agentic AI manages dynamic, high-judgment, or exception-heavy parts of the workflow. Source Source
For example, you might use traditional automation for routine data collection, then hand off to agentic AI to analyze that data and make decisions about how to respond. The result? A system that's efficient, intelligent, and scalable.
The Future is Intelligent
So, how is agentic AI different from traditional automation? The answer spans every dimension: decision-making, autonomy, learning, adaptability, scope, human involvement, and maintenance. Traditional automation is powerful for what it was designed to do—handle repetitive, predictable tasks efficiently. But agentic AI represents the next evolutionary step in automation technology.
Agentic AI systems can think, learn, adapt, and solve problems in ways traditional automation simply cannot. They work toward goals rather than just executing scripts. They improve with experience. They handle complexity and uncertainty. They operate independently with minimal human oversight.
The transformation is already happening across customer service, testing, data operations, and business strategy. Organisations that understand this difference and adapt their automation strategies accordingly will have a significant competitive advantage in the years ahead.
The question isn't whether agentic AI will transform your business—it's how quickly you'll embrace it. The future of automation isn't about following instructions anymore. It's about intelligence, learning, and autonomous problem-solving. And that future is here.
Ready to transform your business with AI?
Let's discuss how we can help you implement custom AI automation solutions
Get in Touch